正文
简述
TreeMap底层是红黑树,在java8 HashMap也引入了红黑树,那么什么是红黑树?红黑树是一种二叉搜索树,它在每个结点上增加了一个存储位来表示结点的颜色,可以是RED或BLACK。通过对任何一条从根到叶子的简单路径上各个结点的颜色进行约束,红黑树确保没有一条路径会比其他路径长出2倍,因而是近似于平衡的。(出自算法导论)
树

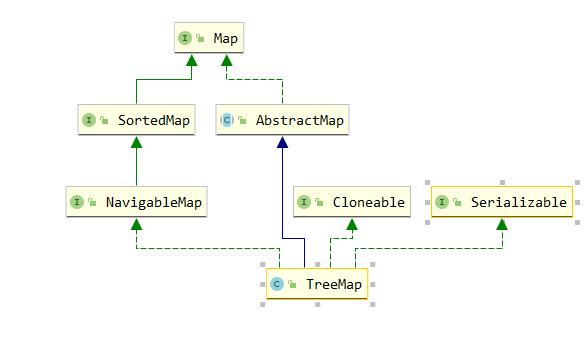
继承关系
TreeMap重要字段
// 比较器用于排序,若为null使用自然排序维持key顺序
private final Comparator comparator;
// 根节点
private transient Entry root;
// 节点数
private transient int size = 0;
// 修改次数,fail-fast
private transient int modCount = 0;
//节点颜色
private static final boolean RED = false;
private static final boolean BLACK = true;
/**
* 节点
*/
static final class Entry implements Map.Entry {
K key; //键
V value; //值
Entry left; //左子树
Entry right; //右子树
Entry parent; //父亲
boolean color = BLACK; //颜色
Entry(K key, V value, Entry parent) {...}
public K getKey() {...}
public V getValue() {...}
public V setValue(V value) {...}
public boolean equals(Object o) {...}
public int hashCode() {...}
public String toString() {...}
}
构造方法
/**
* 无参构造,自然排序(从小到大)。要求key实现Comparable接口,会调用key重写的compareTo方法进行比较
* 若key没有实现comparable接口,运行时报错(java.lang.ClassCastException)
*/
public TreeMap() {
comparator = null;
}
/**
* 指定比较器,若不为null会调用其compare方法进行比较,无需键实现comparable接口
*/
public TreeMap(Comparator comparator) {
this.comparator = comparator;
}
/**
* 将map转为treeMap,比较器为null,注意key
*/
public TreeMap(Map m) {
comparator = null;
putAll(m);
}
/**
* 将map转为treeMap,比较器为SortMap中的comparator
*/
public TreeMap(SortedMap m) {
comparator = m.comparator();
try {
buildFromSorted(m.size(), m.entrySet().iterator(), null, null);
} catch (java.io.IOException cannotHappen) {
} catch (ClassNotFoundException cannotHappen) {
}
}
put方法
public V put(K key, V value) {
// 获取根节点
Entry t = root;
// 若TreeMap为空则直接插入
if (t == null) {
//校验:若比较器为null则key必须实现Comparable接口,若不为null,key可为null
compare(key, key); // type (and possibly null) check
//设为头节点
root = new Entry<>(key, value, null);
size = 1;
modCount++;
return null;
}
// 记录key排序比较结果
int cmp;
// 记录父节点
Entry parent;
// split comparator and comparable paths
Comparator cpr = comparator;
// 若存在比较器,循环查找位置cmp小于0往左找,大于0往右找,直至等于0进行替换
if (cpr != null) {
do {
parent = t;
cmp = cpr.compare(key, t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
// 若不存在比较器,key必须实现Comparable接口
else {
//null无法实现Comparable接口没有compareTo方法故抛异常
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//获取比较器,处理方式与上面一致
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable k = (Comparable) key;
do {
parent = t;
cmp = k.compareTo(t.key);
if (cmp < 0)
t = t.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
t = t.right;
else
return t.setValue(value);
} while (t != null);
}
//若当前TreeMap中没有此key则新建结点,无论上述哪个分支成立parent一定指向当前某个叶子结点
Entry e = new Entry<>(key, value, parent);
//小于0则为左子树
if (cmp < 0)
parent.left = e;
//大于0则为右子树
else
parent.right = e;
//保证红黑树性质
fixAfterInsertion(e);
size++;
modCount++;
return null;
}
get方法
get方法与put思路大致相同
public V get(Object key) {
Entry p = getEntry(key);
//找到对应节点返回其值,没有找到返回null
return (p==null ? null : p.value);
}
final Entry getEntry(Object key) {
// Offload comparator-based version for sake of performance
// 若比较器不为null
if (comparator != null)
return getEntryUsingComparator(key);
// 若比较器为null,则key必须实现Comparable接口,null不能抛异常
if (key == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
//用key的compareTo方法,从根节点寻找,若没有找返回null
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
Comparable k = (Comparable) key;
Entry p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = k.compareTo(p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
return null;
}
final Entry getEntryUsingComparator(Object key) {
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
K k = (K) key;
Comparator cpr = comparator;
//处理方式一致
if (cpr != null) {
Entry p = root;
while (p != null) {
int cmp = cpr.compare(k, p.key);
if (cmp < 0)
p = p.left;
else if (cmp > 0)
p = p.right;
else
return p;
}
}
return null;
}
containsValue方法
采用类似中序遍历(LDR左根右)方式来遍历整个红黑树找到相应value
public boolean containsValue(Object value) {
for (Entry e = getFirstEntry(); e != null; e = successor(e))
if (valEquals(value, e.value))
return true;
return false;
}
/**
* 返回最小节点
*/
final Entry getFirstEntry() {
Entry p = root;
if (p != null)
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
}
/**
* 找后继节点
*/
static TreeMap.Entry successor(Entry t) {
if (t == null)
return null;
//若存在右子树,则返回右子树中最小节点
else if (t.right != null) {
Entry p = t.right;
while (p.left != null)
p = p.left;
return p;
//若不存在,从当前节点往上找,若其父节点不为null且它是父节点的右子树则继续找父节点
//直至条件不成立,返回父节点
} else {
Entry p = t.parent;
Entry ch = t;
while (p != null && ch == p.right) {
ch = p;
p = p.parent;
}
return p;
}
}
successor方法找节点的后继节点: ①.若节点为空没有后继 ②.若节点有右子树,后继为右子树的最左节点 ③.若节点没有右子树,后继为该节点所在左子树的第一个祖先节点
第一个无需多言,第二个也容易,看图p的后继节点s:
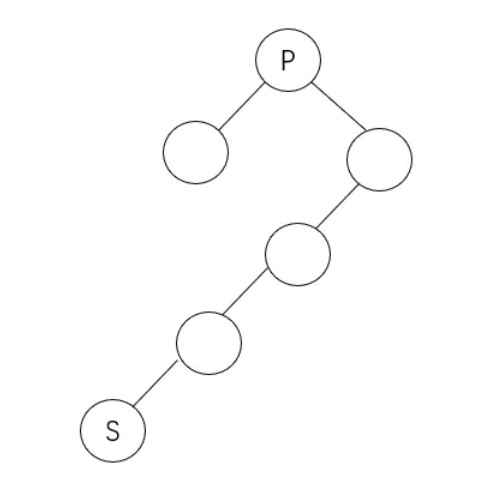
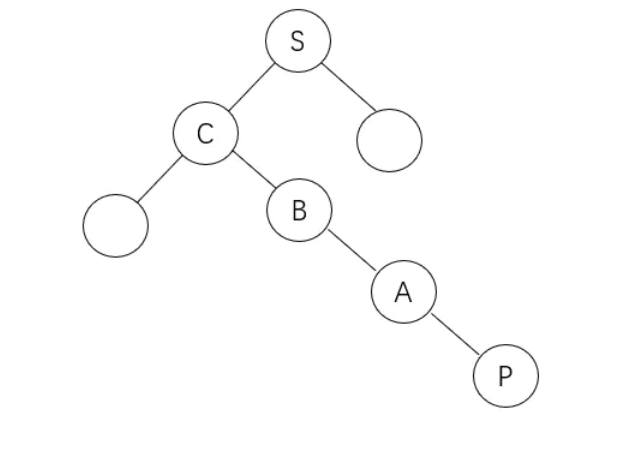
第三个: 若其父节点为空,返回null; 若其有父节点且为父节点左子树,返回其父节点; 若其有父节点且为父节点右子树,其所在左子树的第一个祖先节点看图(p的后继为s),一个个往上找将p与A看成整体相对于B是其右子树,再往上找将P、B、A看成整体相对于C还是其右子树,再找P、B、A、C整体相对于S是其左子树,返回这个整体的第一个祖先节点即节点S
remove方法
public V remove(Object key) {
//获取key所对应的节点
Entry p = getEntry(key);
//若节点为空返回null
if (p == null)
return null;
//若不为null,删除节点返回其值
V oldValue = p.value;
deleteEntry(p);
return oldValue;
}
private void deleteEntry(Entry p) {
modCount++;
size--;
//若p左子树和右子树都不为null,将p的key与value替换成后继的,将p指向后继
if (p.left != null && p.right != null) {
Entry s = successor(p);
p.key = s.key;
p.value = s.value;
p = s;
} // p has 2 children
// replacement为替代节点
Entry replacement = (p.left != null ? p.left : p.right);
if (replacement != null) {
replacement.parent = p.parent;
//若p没有父节点,则根节点设为replacement
if (p.parent == null)
root = replacement;
//若p为左节点,则用replacement替换左节点
else if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = replacement;
//若p为右节点,则用replacement替换右节点
else
p.parent.right = replacement;
//删除p节点
p.left = p.right = p.parent = null;
// 若p为黑色则需要调整
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(replacement);
//若p没有父节点即p为根节点,根节点置空
} else if (p.parent == null) { // return if we are the only node.
root = null;
//p没有子节点
} else { // No children. Use self as phantom replacement and unlink.
if (p.color == BLACK)
fixAfterDeletion(p);
//删除p节点
if (p.parent != null) {
if (p == p.parent.left)
p.parent.left = null;
else if (p == p.parent.right)
p.parent.right = null;
p.parent = null;
}
}
}
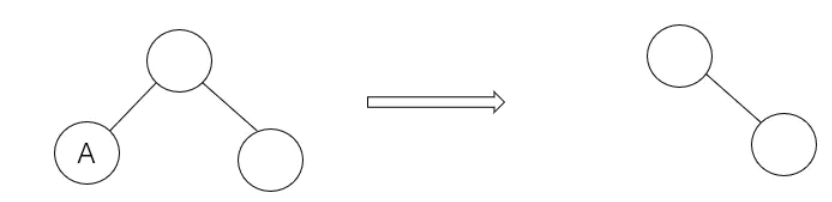
分三种情况: ①.叶子结点:直接将其父节点对应孩子置空,若删除左叶子结点则将其父结点左子树置空,若删除右叶子结点则将其父结点右子树置空
删除节点A:
②.一个孩子:用子节点替代需删除节点
删除节点G:
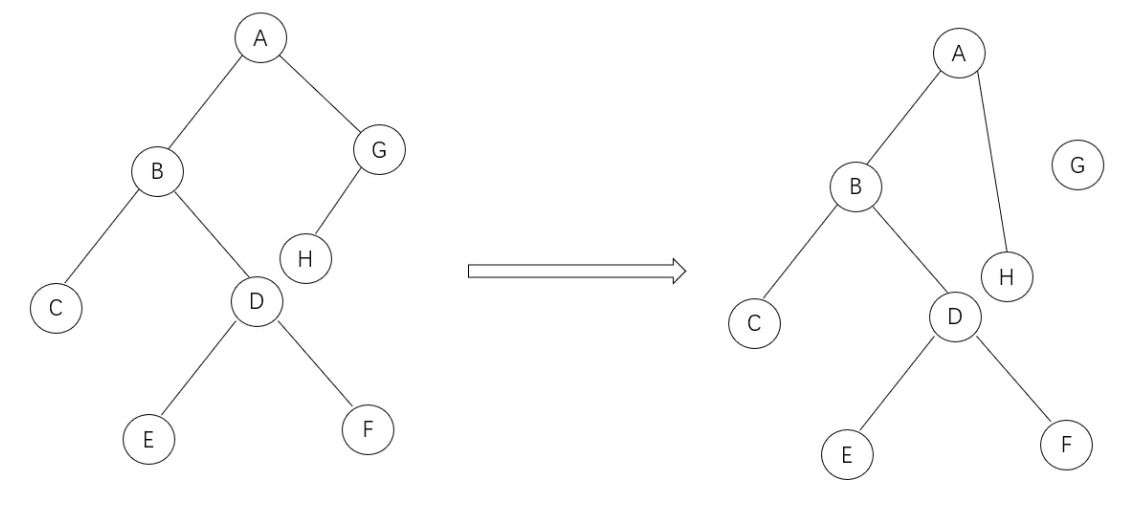
③.两个孩子:先找到后继,找到后,替换当前节点的内容为后继节点,然后再删除后继节点,因为这个后继节点一定没有左孩子,所以就将两个孩子的情况转换为了前面两种情况
删除节点B:
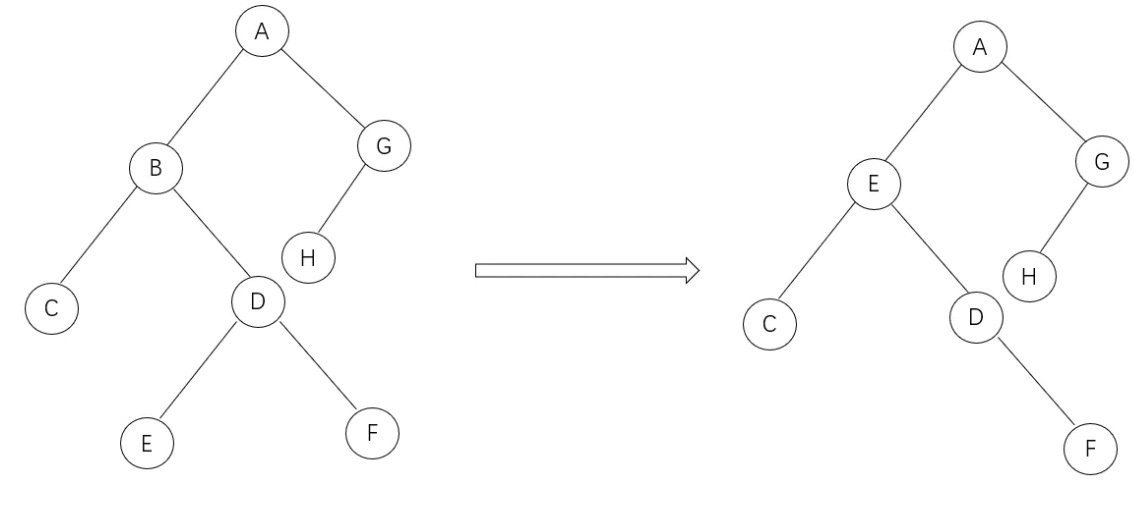
小结
①.TreeMap底层是红黑树,集合有序线程不安全。 ②.若比较器为空则key一定不能为null,若比较器不为空则key可以为null由TreeMap其比较器而定 ③.containsValue方法采用中序遍历(LDR左根右)方式遍历整个TreeMap 在上一篇文章(java8HashMap)写了链表与红黑树互转,本文略微提及红黑树相关知识主要围绕源码讲述TreeMap的一些方法,下篇主要以TreeMap插入删除后如何维持其特性。
参考: