题003 二维数组中的查找
复杂问题从具体问题入手,分析简单例子,找出规律
在一个 n * m 的二维数组中,每一行都按照从左到右递增的顺序排序,每一列都按照从上到下递增的顺序排序。请完成一个函数,输入这样的一个二维数组和一个整数,判断数组中是否含有该整数。
示例:
现有矩阵 matrix 如下:
[
[1, 4, 7, 11, 15],
[2, 5, 8, 12, 19],
[3, 6, 9, 16, 22],
[10, 13, 14, 17, 24],
[18, 21, 23, 26, 30]
]
给定 target = 5,返回 true。
给定 target = 20,返回 false。
代码:
public boolean findNumberIn2DArray(int[][] matrix, int target) {
if (matrix == null || matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return false;
}
int rowLength = matrix.length; //总行数
int colLength = matrix[0].length; //总列数
int currentRow = 0; //起始位置是右上角 行号是0
int currentCol = colLength - 1; //起始位置是右上角 列号最大值
while (currentRow < rowLength && currentCol >= 0) {//防止越界
if (matrix[currentRow][currentCol] == target) {
return true;
} else if (matrix[currentRow][currentCol] > target)//比要找的数大 排除这一列
{
currentCol--;
} else { //比要找的数小 排除更小的数 排除这一行
currentRow++;
}
}
return false;
}
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n+m)。访问到的下标的行最多增加 n 次,列最多减少 m 次,因此循环体最多执行 n + m 次。
题004 替换空格
从头到尾扫描字符串碰到空格替换, 需要空格后面的·字符都移动移动字符串 时间复杂度 O(n^2)
优化方案:
优化的方法是先遍历一编字符串,知道字符串的空格数,然后计算得到替换后的长度=原来长度+2*空格数,然后从字符串的末尾进行遍历,每次把元素移动到计算后的数组下标的位置,并且对空格进行替换。
代码:
public String replaceSpace(String s) {
int cnt = 0;// 空格数
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (s.charAt(i) == ' ') {
cnt++;
}
}
int oldLength = s.length();
int newLength = s.length() + 2 * cnt;//新字符串长度
StringBuilder str = new StringBuilder();
str.setLength(newLength);
int newIndex = newLength - 1;
for (int i = oldLength - 1; i >= 0; i--) {//倒序遍历
if (s.charAt(i) != ' ') {
str.setCharAt(newIndex, s.charAt(i));
newIndex--;
} else {
str.setCharAt(newIndex, '0');
str.setCharAt(newIndex - 1, '2');
str.setCharAt(newIndex - 2, '%');
newIndex = newIndex - 3;
}
}
return str.toString();
}
注意内存覆盖
合并两个数组包括字符串时,如果从前往后复制每个数字需要重复移动数字多次,可以考虑从后往前复制,减少移动次数
题005 从尾到头打印链表
输入一个链表的头节点,从尾到头反过来返回每个节点的值(用数组返回)。
示例 1:
输入:head = [1,3,2]
输出:[2,3,1]
public int[] reversePrint(ListNode head) {
Stack<ListNode> stack = new Stack<>();
ListNode dummyHead = head;
while (dummyHead != null) {
stack.push(dummyHead);
dummyHead = dummyHead.next;
}
int size = stack.size();
int[] result = new int[size];
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
result[i] = stack.pop().val;
}
return result;
}
题006重建二叉树
二叉树的前序遍历顺序是:根节点、左子树、右子树,每个子树的遍历顺序同样满足前序遍历顺序。
二叉树的中序遍历顺序是:左子树、根节点、右子树,每个子树的遍历顺序同样满足中序遍历顺序。
方法:分治思想
二叉树的问题一般都是分治思想,递归去做。因为二叉树本身就是递归实现的
解题思路:
前序遍历的第 1 个结点一定是二叉树的根结点; 在中序遍历中,根结点把中序遍历序列分成了两个部分,左边部分构成了二叉树的根结点的左子树,右边部分构成了二叉树的根结点的右子树。 查找根结点在中序遍历序列中的位置,可以遍历,也可以在一开始就记录下来。
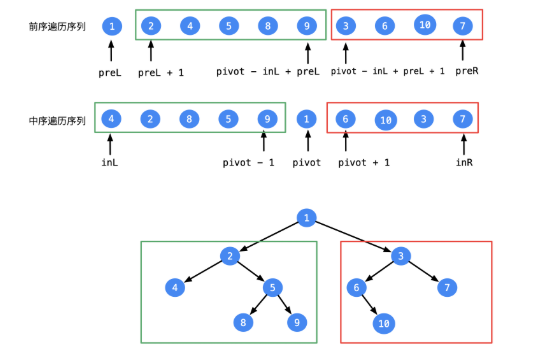
public class Solution {
// 使用全局变量是为了让递归方法少传一些参数,不一定非要这么做
private Map<Integer, Integer> reverses;
private int[] preorder;
public TreeNode buildTree(int[] preorder, int[] inorder) {
int preLen = preorder.length;
int inLen = inorder.length;
// 可以不做判断,因为题目中给出的数据都是有效的
if (preLen != inLen) {
return null;
}
this.preorder = preorder;
// 以空间换时间,否则,找根结点在中序遍历中的位置需要遍历
reverses = new HashMap<>(inLen);
for (int i = 0; i < inLen; i++) {
reverses.put(inorder[i], i);
}
return buildTree(0, preLen - 1, 0, inLen - 1);
}
/**
* 根据前序遍历数组的 [preL, preR] 和 中序遍历数组的 [inL, inR] 重新组建二叉树
*
* @param preL 前序遍历数组的区间左端点
* @param preR 前序遍历数组的区间右端点
* @param inL 中序遍历数组的区间左端点
* @param inR 中序遍历数组的区间右端点
* @return 构建的新二叉树的根结点
*/
private TreeNode buildTree(int preL, int preR,
int inL, int inR) {
if (preL > preR || inL > inR) {
return null;
}
// 构建的新二叉树的根结点一定是前序遍历数组的第 1 个元素
int pivot = preorder[preL];
TreeNode root = new TreeNode(pivot);
int pivotIndex = reverses.get(pivot);
// 这一步得画草稿,计算边界的取值,必要时需要解方程,并不难
root.left = buildTree(preL + 1, preL + (pivotIndex - inL), inL, pivotIndex - 1);
root.right = buildTree(preL + (pivotIndex - inL) + 1, preR, pivotIndex + 1, inR);
return root;
}
}
题007两个栈实现队列
现在栈的实现最好就是用Deque
Stack性能不高
- 所有操作都是同步的(当然,在题目的单线程场景下,锁可能会被优化掉)
- 内部用数组来装元素,所以需要扩容,但是“栈”的读写操作都是在栈顶,不需要数组的随机访问,所以用链表来实现栈更合适
class CQueue {
Deque<Integer> stack1;
Deque<Integer> stack2;
public CQueue() {
stack1 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
stack2 = new LinkedList<Integer>();
}
public void appendTail(int value) {
stack1.push(value);
}
public int deleteHead() {
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
while (!stack1.isEmpty()) {
stack2.push(stack1.pop());
}
}
if (stack2.isEmpty()) {
return -1;
} else {
return stack2.pop();
}
}
}
题008旋转数组的最小数字
有序数组查找 优先考虑二分法(顺序查找 元素有序)
把一个数组最开始的若干个元素搬到数组的末尾,我们称之为数组的旋转。输入一个递增排序的数组的一个旋转,输出旋转数组的最小元素。例如,数组 [3,4,5,1,2] 为 [1,2,3,4,5] 的一个旋转,该数组的最小值为1。
示例 1:
输入:[3,4,5,1,2]
输出:1
思路:
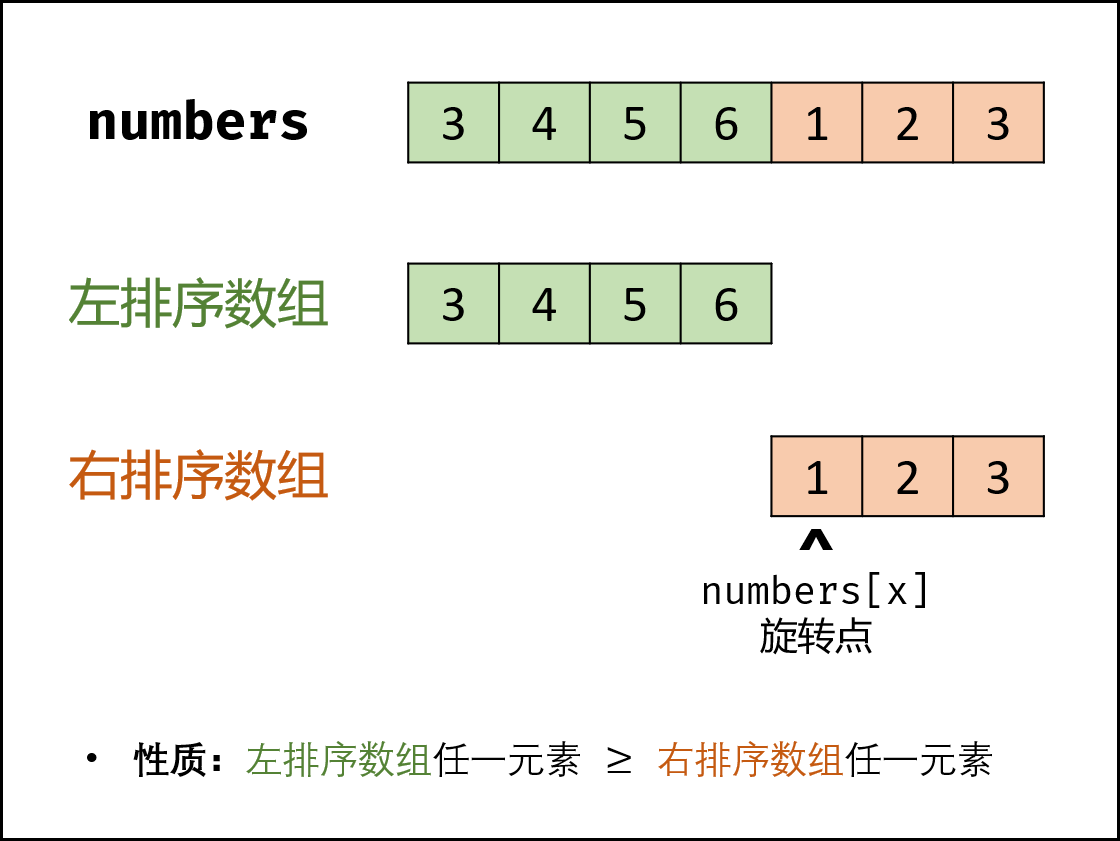
代码:
public int minArray(int[] numbers) {
int low = 0;
int height = numbers.length - 1;
while (low < height) {
int mid = low + (height - low) / 2; //不适用(low+height)/2 防止溢出
if (numbers[mid] < numbers[height]) { //mid一定在右序列 旋转点一定在[left,mid]之间
height = mid;
} else if (numbers[mid] > numbers[height]) { //mid一定在左序列,旋转点一定在[mid+1,height]之间
low = mid + 1;
} else { //nums[l] == nums[m] == nums[h],此时无法确定解在哪个区间,需要切换到顺序查找
height--;
}
}
return numbers[low];
}
题009-1斐波那契数列
写一个函数,输入 n ,求斐波那契(Fibonacci)数列的第 n 项。斐波那契数列的定义如下:
F(0) = 0, F(1) = 1 F(N) = F(N - 1) + F(N - 2), 其中 N > 1. 斐波那契数列由 0 和 1 开始,之后的斐波那契数就是由之前的两数相加而得出。
答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007),如计算初始结果为:1000000008,请返回 1。
递归
int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n == 0){
return 0;
} else if (n==1) {
return 1;
}
return Fibonacci(n-1) + Fibonacci(n-2);
}
递归是将一个问题划分成多个子问题求解,动态规划也是如此,但是动态规划会把子问题的解缓存起来,从而避免重复求解子问题。
public int Fibonacci(int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
int[] fib = new int[n + 1];
fib[1] = 1;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++)
fib[i] = fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2];
return fib[n];
}
考虑到第 i 项只与第 i-1 和第 i-2 项有关,因此只需要存储前两项的值就能求解第 i 项,从而将空间复杂度由 O(N) 降低为 O(1)。
public int fib(int n) {
if (n <= 1) {
return n;
}
int a1 = 0, a2 = 1, sum = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
sum = (a1 + a2) % 1000000007;
a1 = a2;
a2 = sum;
}
return sum;
}
题009-2青瓜跳台阶问题
一只青蛙一次可以跳上1级台阶,也可以跳上2级台阶。求该青蛙跳上一个 n 级的台阶总共有多少种跳法。
答案需要取模 1e9+7(1000000007),如计算初始结果为:1000000008,请返回 1。
示例 1:
输入:n = 2 输出:2
public int numWays(int n) {
if (n == 0 || n == 1) {
return 1;
}
int[] fib = new int[n + 1];
fib[1] = 1;
fib[2] = 2;
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
fib[i] = (fib[i - 1] + fib[i - 2]) % 1000_000_007;
}
return fib[n];
}
题010二进制中1的个数
请实现一个函数,输入一个整数,输出该数二进制表示中 1 的个数。例如,把 9 表示成二进制是 1001,有 2 位是 1。因此,如果输入 9,则该函数输出 2。
示例 1:
输入:00000000000000000000000000001011
输出:3
解释:输入的二进制串 00000000000000000000000000001011 中,共有三位为 '1'。
解法一:
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int count = 0;
while (n != 0) {
count += n & 1; //判断 nn 最右一位是否为 11 ,根据结果计数。
n >>>= 1; //本题要求把数字 nn 看作无符号数,因此使用 无符号右移 操作
}
return count;
}
解法二:巧用 n \& (n - 1)
(n−1) 解析: 二进制数字 nn 最右边的 11 变成 00 ,此 11 右边的 00 都变成 11 。 n \& (n - 1)n&(n−1) 解析: 二进制数字 nn 最右边的 11 变成 00 ,其余不变。
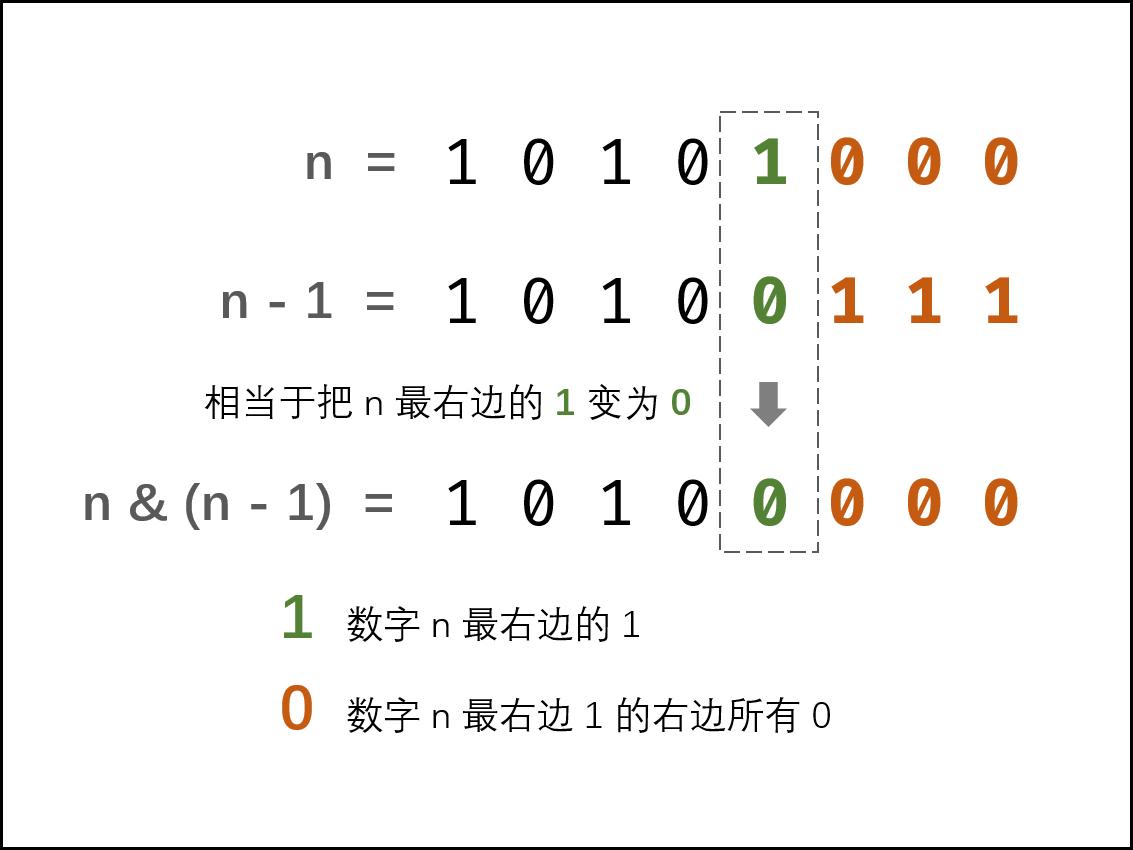
public int hammingWeight(int n) {
int res = 0;
while(n != 0) {
res++;
n &= n - 1; //循环消去最右边的 11 :当 n = 0n=0 时跳出
}
return res;
}
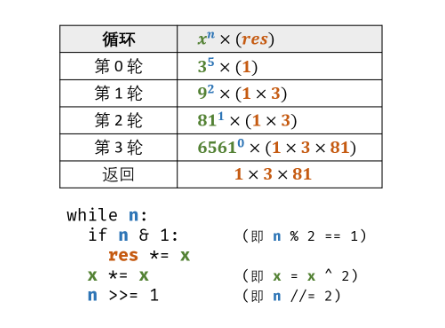
题011数值的整数次方
实现函数double Power(double base, int exponent),求base的exponent次方。不得使用库函数,同时不需要考虑大数问题。
示例 1:
输入: 2.00000, 10
输出: 1024.00000
解法:二分法思想
当我们指数是32,我们需要最31次乘法。 但我们可以换一种思路。 我们可以知道它的16次方,然后再16次方的基础上平方一次就行。而16是8平方的平方,依次递推
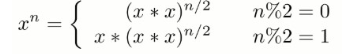
public double myPow(double x, int n) {
if (x == 0) {
return 0; //0无意义
}
long b = n; //Java 代码中 int32 当 n = -2147483648n=−2147483648 时执行 n = -n 会因越界而赋值出错。
double res = 1.0;
if (b < 0) {
x = 1 / x;
b = -b;
}
while (b > 0) {
if ((b & 1) == 1) { // n%2==1
res = res * x; // n是奇数
}
x = x * x;
b = b >> 1; // n/2
}
return res;
}
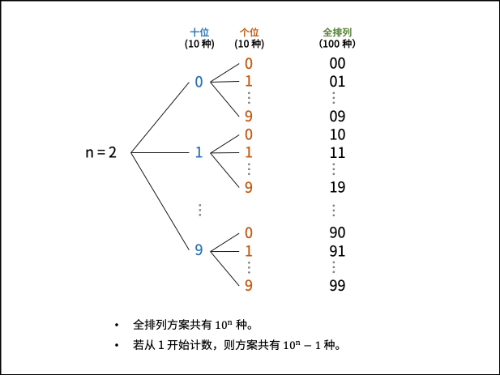
题012打印从1到最大的n位数
输入数字 n,按顺序打印出从 1 到最大的 n 位十进制数。比如输入 3,则打印出 1、2、3 一直到最大的 3 位数 999。
示例 1:
输入: n = 1
输出: [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9]
大数打印解法:
- 表示大数的变量类型
无论是 short / int / long … 任意变量类型,数字的取值范围都是有限的。因此,大数的表示应用字符串 String 类型。
2.生成数字的字符串集:
String 无法加1
3.递归生成全排列
基于分治算法思想,固定高位向低位递归
int[] res;
int n,count = 0;
char[] num, loop = { '0','1', '2', '3', '4', '5', '6', '7', '8', '9'};
public int[] printNumbers(int n) {
this.n = n;
res = new int[(int)Math.pow(10, n) - 1];; // 数字字符串集
num = new char[n]; // 定义长度为 n 的字符列表
dfs(0); // 开启全排列递归
return res;
}
void dfs(int x) {
if (x == n) { // 终止条件:已固定完所有位
Integer num2 = Integer.valueOf(String.valueOf(num));
if (num2 != 0) {
res[count++] = num2;; // 拼接 num 并添加至 res 尾部,使用逗号隔开
}
return;
}
for (char i : loop) { // 遍历 ‘0‘ - ’9‘
num[x] = i; // 固定第 x 位为 i
dfs(x + 1); // 开启固定第 x + 1 位
}
}
题013删除链表的节点
给定单向链表的头指针和一个要删除的节点的值,定义一个函数删除该节点。
返回删除后的链表的头节点。
注意:此题对比原题有改动
示例 1:
输入: head = [4,5,1,9], val = 5
输出: [4,1,9]
解释: 给定你链表中值为 5 的第二个节点,那么在调用了你的函数之后,该链表应变为 4 -> 1 -> 9.
public ListNode deleteNode(ListNode head, int val) {
if (head == null) {
return null;
}
if (head.val == val) {
return head.next;
}
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur.next != null && cur.next.val != val) {
cur = cur.next;
}
if (cur.next != null) {
cur.next = cur.next.next;
}
return head;
}
题014调整数组顺序使奇数位于偶数前面
输入一个整数数组,实现一个函数来调整该数组中数字的顺序,使得所有奇数位于数组的前半部分,所有偶数位于数组的后半部分。
示例:
输入:nums = [1,2,3,4]
输出:[1,3,2,4]
注:[3,1,2,4] 也是正确的答案之一。
首尾双指针
-
定义头指针 left,尾指针 right
-
left 一直往右移,直到它指向的值为偶数
-
right 一直往左移, 直到它指向的值为奇数、
-
交换 nums[left和nums[right] .
-
重复上述操作,直到 left == right .
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) { int left = 0; int right = nums.length - 1; while (left < right) { if ((nums[left] & 1) != 0) { left++; continue; } if ((nums[right] & 1) != 1) { right--; continue; } int temp = nums[left]; nums[left] = nums[right]; nums[right] = temp; left++; right--; } return nums; }
快慢双指针
- 定义快慢双指针 fast和 low ,fast 在前, low 在后 .
- fast 的作用是向前搜索奇数位置,low的作用是指向下一个奇数应当存放的位置
- fast 向前移动,当它搜索到奇数时,将它和 nums[low] 交换,此时 low 向前移动一个位置 .
- 重复上述操作,直到 fast指向数组末尾 .
public int[] exchange(int[] nums) {
int low = 0,fast = 0;
while (fast < nums.length) {
if ((nums[fast] & 1) == 1) {
int temp = nums[low];
nums[low] = nums[fast];
nums[fast] = temp;
low++; //交换之后low才向前移动
}
fast++;
}
return nums;
}
题015链表中倒数第k个节点
输入一个链表,输出该链表中倒数第k个节点。为了符合大多数人的习惯,本题从1开始计数,即链表的尾节点是倒数第1个节点。例如,一个链表有6个节点,从头节点开始,它们的值依次是1、2、3、4、5、6。这个链表的倒数第3个节点是值为4的节点。
示例:
给定一个链表: 1->2->3->4->5, 和 k = 2.
返回链表 4->5.
前后指针
前指针先向前走k步,然后前后指针共同移动,直到前指针走过链表尾节点时跳出 返回后指针
时间复杂度O(N)
public ListNode getKthFromEnd(ListNode head, int k) {
ListNode front = head, back = head;
for (int i = 0; i < k; i++) {
front = front.next;
}
while (front != null) {
front = front.next;
back = back.next;
}
return back;
}
题016反转链表
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头节点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头节点。
示例:
输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL
输出: 5->4->3->2->1->NULL
双指针
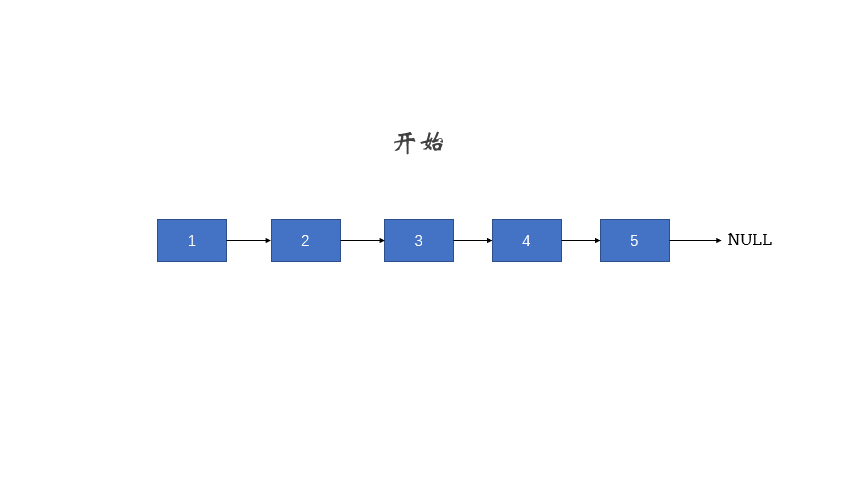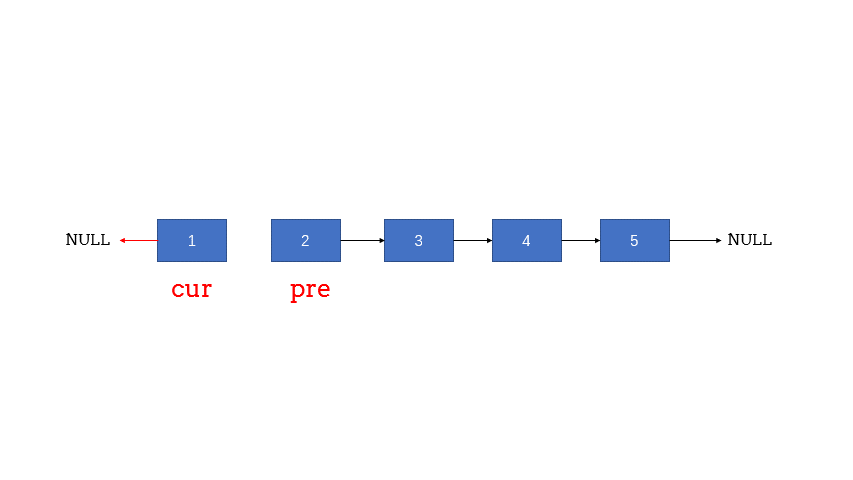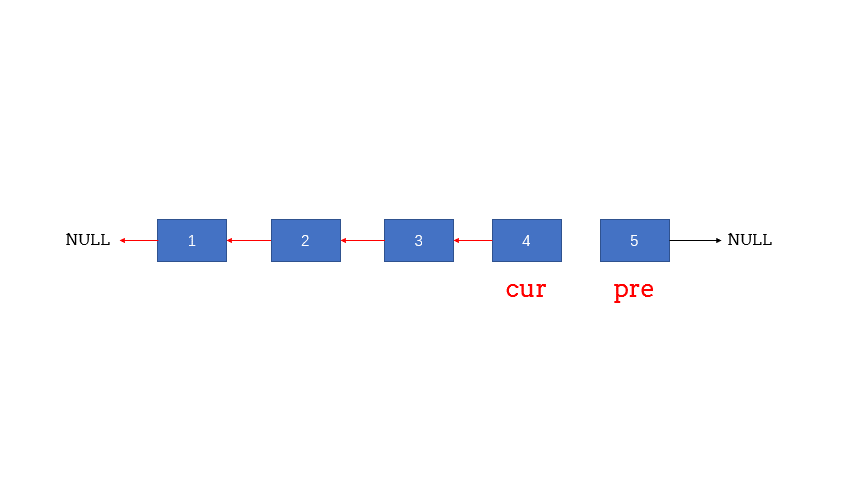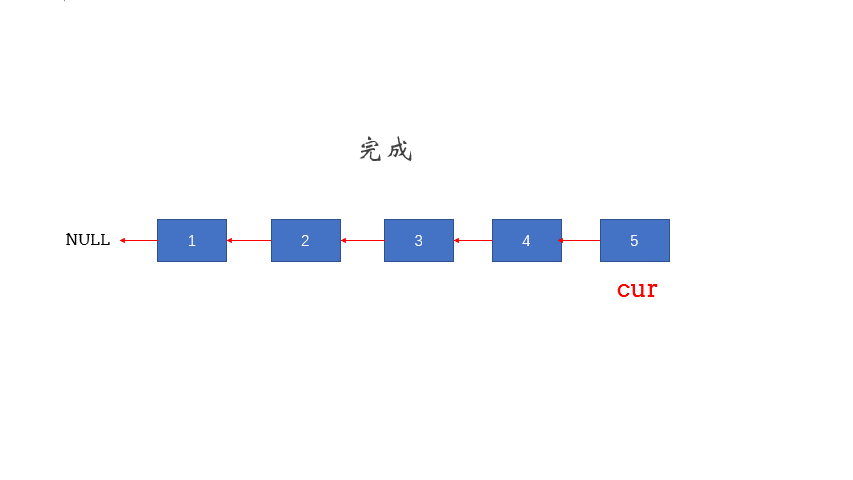
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode cur = null, pre = head;
while (pre != null) {
ListNode temp = pre.next; //由于指针变动 需要先记着节点
pre.next = cur;
cur = pre;
pre = temp;
}
return cur;
}
递归
- 使用递归函数,一直递归到链表的最后一个结点,该结点就是反转后的头结点,记作 ret.
- 此后,每次函数在返回的过程中,让当前结点的下一个结点的 next 指针指向当前节点。
- 同时让当前结点的 next 指针指向 NULL ,从而实现从链表尾部开始的局部反转
- 当递归函数全部出栈后,链表反转完成。
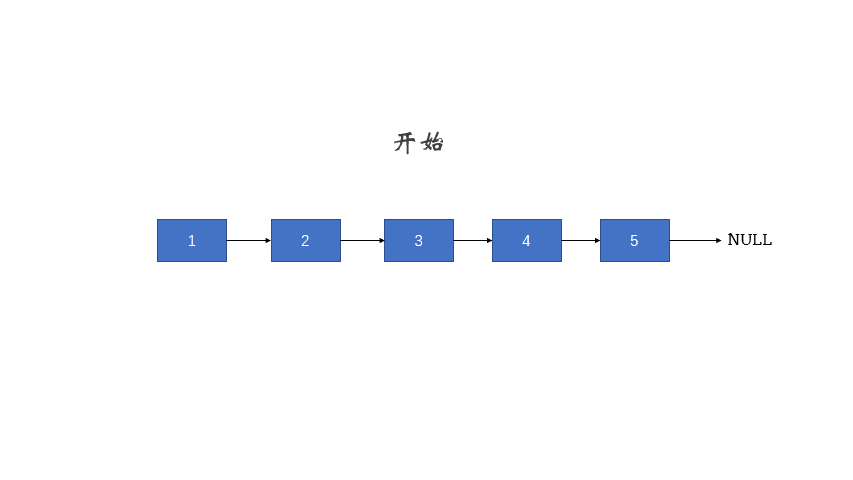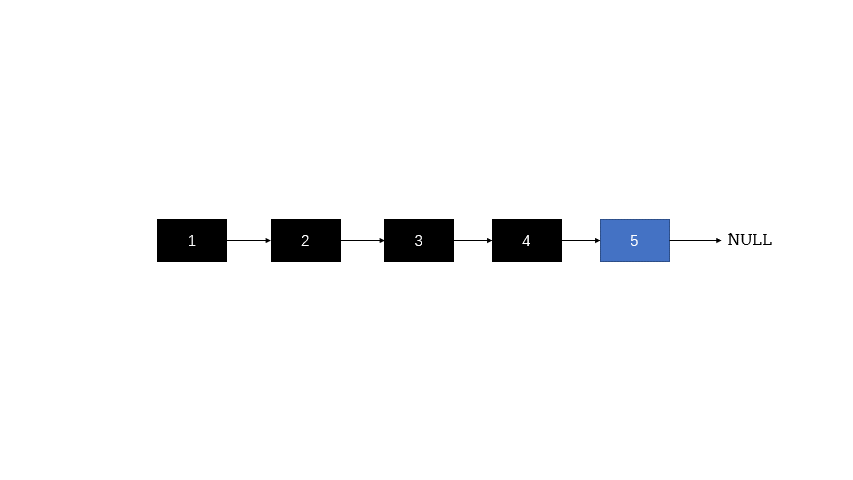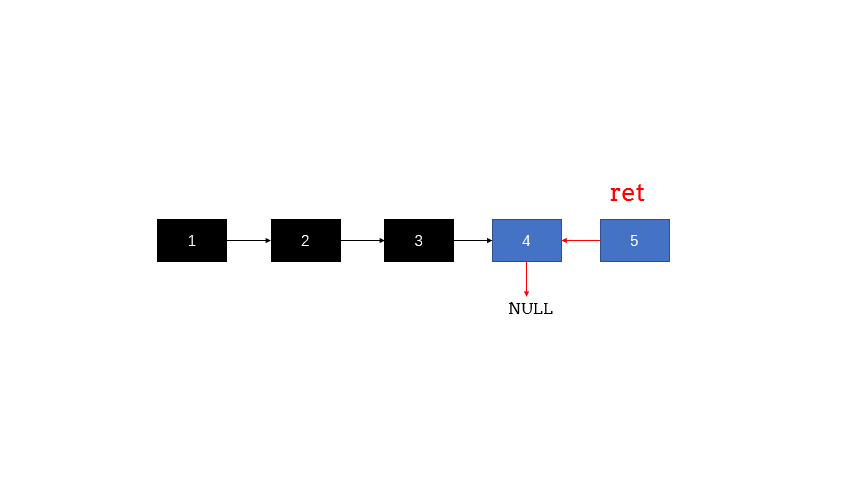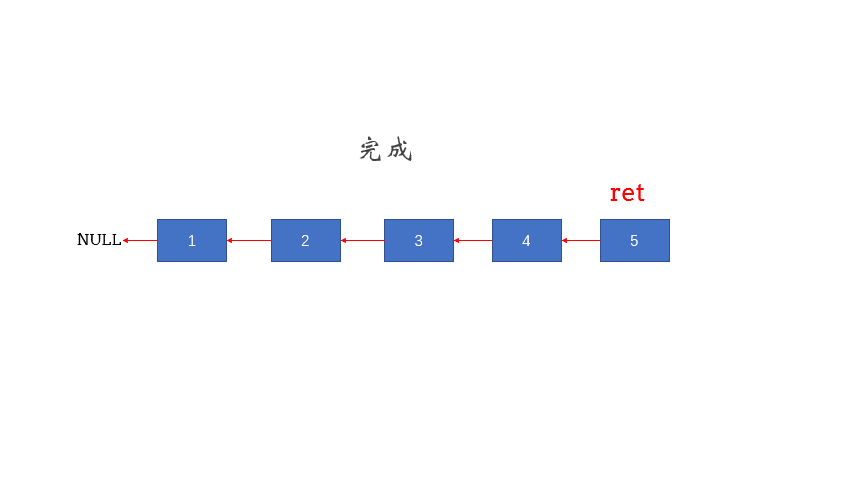
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return head;
}
ListNode ret = reverseList(head.next);
head.next.next = head;
head.next = null;
return ret;
}
题017合并两个排序的链表
输入两个递增排序的链表,合并这两个链表并使新链表中的节点仍然是递增排序的。
示例1:
输入:1->2->4, 1->3->4
输出:1->1->2->3->4->4
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode head = new ListNode(0), cur = head; //由于初始状态链表无节点,引入伪节点
while (l1 != null && l2 != null) { //当某个列表为空 跳出循环
if (l1.val < l2.val) { //当L1的值小的时候 存入 L1指针后移
cur.next = l1;
l1 = l1.next;
} else { //l2小 l2存入 L2指针后移
cur.next = l2;
l2 = l2.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
cur.next = l1 != null ? l1 : l2; // 跳出时有两种情况 即l1为空 或 l2为空
return head.next;
}
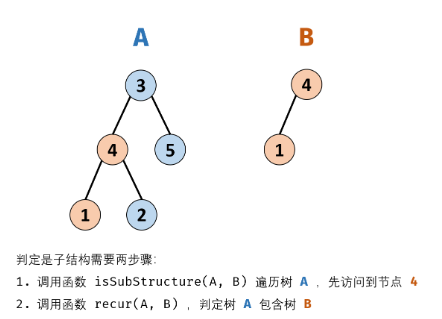
题018树的子结构
输入两棵二叉树A和B,判断B是不是A的子结构。(约定空树不是任意一个树的子结构)
B是A的子结构, 即 A中有出现和B相同的结构和节点值。
例如: 给定的树 A:
3
/ \
4 5
/ \
1 2
给定的树 B:
4
/
1
返回 true,因为 B 与 A 的一个子树拥有相同的结构和节点值。
示例 1:
输入:A = [1,2,3], B = [3,1]
输出:false
示例 2:
输入:A = [3,4,5,1,2], B = [4,1]
输出:true
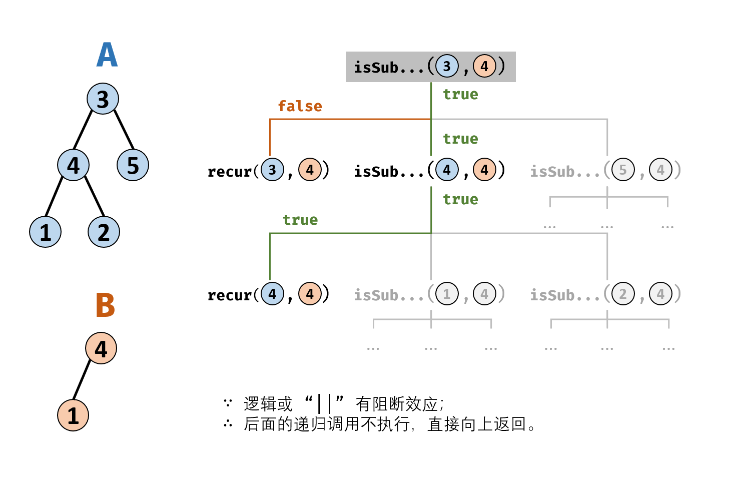
public boolean isSubStructure(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
return (A != null && B != null) && (recur(A, B) || isSubStructure(A.left, B) || isSubStructure(A.right, B));
}
boolean recur(TreeNode A, TreeNode B) {
if (B == null) {
return true;
}
if (A == null || A.val != B.val) {
return false;
}
return recur(A.left, B.left) && recur(A.right, B.right);
}
题019二叉树的镜像
请完成一个函数,输入一个二叉树,该函数输出它的镜像。
例如输入:
4
/ \
2 7
/ \ / \
1 3 6 9
镜像输出:
4
/ \
7 2
/ \ / \
9 6 3 1 示例 1:
输入:root = [4,2,7,1,3,6,9]
输出:[4,7,2,9,6,3,1]
递归法
public TreeNode mirrorTree(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return null;
}
TreeNode temp = root.left; //缓存是因为 执行后 left值发生变化
root.left = mirrorTree(root.right);
root.right = mirrorTree(temp);
return root;
}
题020 顺时针打印矩阵
输入一个矩阵,按照从外向里以顺时针的顺序依次打印出每一个数字。
示例 1:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3],[4,5,6],[7,8,9]]
输出:[1,2,3,6,9,8,7,4,5]
示例 2:
输入:matrix = [[1,2,3,4],[5,6,7,8],[9,10,11,12]]
输出:[1,2,3,4,8,12,11,10,9,5,6,7]
解法:
public int[] spiralOrder(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0) {
return new int[0];
}
// 矩阵 左、右、上、下 四个边界 l , r , t , b
int l = 0, r = matrix[0].length - 1, t = 0, b = matrix.length - 1, x = 0;
int[] res = new int[(r + 1) * (b + 1)];
while (true) {
for (int i = l; i <= r; i++) {
res[x++] = matrix[t][i]; // 从左到右 上边界加一
}
if (++t > b) {
break;
}
for (int i = t; i <= b; i++) {
res[x++] = matrix[i][r]; // 从上到小 右边界减一
}
if (l > --r) {
break;
}
for (int i = r; i >= l; i--) {
res[x++] = matrix[b][i]; // 从右向左 下边界减一
}
if (t > --b) {
break;
}
for (int i = b; i >= t; i--) {
res[x++] = matrix[i][l]; // 从下向上 左边界加一
}
if (++l > r) {
break;
}
}
return res;
}
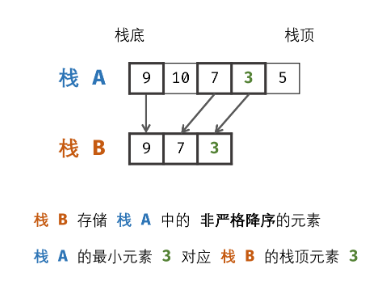
题021包含min的函数栈
定义栈的数据结构,请在该类型中实现一个能够得到栈的最小元素的 min 函数在该栈中,调用 min、push 及 pop 的时间复杂度都是 O(1)。
示例:
MinStack minStack = new MinStack();
minStack.push(-2);
minStack.push(0);
minStack.push(-3);
minStack.min(); --> 返回 -3.
minStack.pop();
minStack.top(); --> 返回 0.
minStack.min(); --> 返回 -2.
辅助栈
//leetcode submit region begin(Prohibit modification and deletion)
class MinStack {
/**
* initialize your data structure here.
*/
Deque<Integer> A, B;
public MinStack() {
A = new LinkedList<>();
B = new LinkedList<>();
}
public void push(int x) {
A.push(x);
if (B.isEmpty()|| B.peek() >= x) { //当辅助栈为空 或者 辅助栈顶 大于等于入栈值 则入栈
B.push(x);
}
}
public void pop() {
if (A.pop().equals(B.peek())) { //当A的栈顶等于B的栈顶 B出栈
B.pop();
}
}
public int top() {
return A.peek();
}
public int min() {
return B.peek();
}
}
题022栈的压入、弹出序列
输入两个整数序列,第一个序列表示栈的压入顺序,请判断第二个序列是否为该栈的弹出顺序。假设压入栈的所有数字均不相等。例如,序列 {1,2,3,4,5} 是某栈的压栈序列,序列 {4,5,3,2,1} 是该压栈序列对应的一个弹出序列,但 {4,3,5,1,2} 就不可能是该压栈序列的弹出序列。
示例 1:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,5,3,2,1]
输出:true
解释:我们可以按以下顺序执行:
push(1), push(2), push(3), push(4), pop() -> 4,
push(5), pop() -> 5, pop() -> 3, pop() -> 2, pop() -> 1
示例 2:
输入:pushed = [1,2,3,4,5], popped = [4,3,5,1,2]
输出:false
解释:1 不能在 2 之前弹出。
解法: 辅助栈
给定弹入和弹出顺序,则压入和弹出的顺序是唯一确定的
- 元素 num入栈;
- 循环出栈:若 stack 的栈顶元素 == 弹出序列元素 popped[i] ,则执行出栈与 i++
public boolean validateStackSequences(int[] pushed, int[] popped) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
int i = 0;
for (int num : pushed) {
stack.push(num);
// 循环判断 栈顶元素 == 弹出序列元素 则popped[i]
while (!stack.isEmpty() && stack.peek() == popped[i]) {
stack.pop();
i++;
}
}
return stack.isEmpty();
}
题023从上往下打印二叉树
从上到下打印出二叉树的每个节点,同一层的节点按照从左到右的顺序打印。
例如: 给定二叉树: [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回:
[3,9,20,15,7]
解法:BFS 循环 广度优先遍历
- 当队列 queue 为空时跳出;
- 出队: 队首元素出队,记为 node;
- 打印: 将 node.val 添加至列表 tmp 尾部;
- 添加子节点: 若 node 的左(右)子节点不为空,则将左(右)子节点加入队列 queue ;
public int[] levelOrder(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return new int[0];
}
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new LinkedList<>(); //linkedlist 继承deque双端队列接口,可以作为栈或者队列 Deque是Queue子接口
queue.add(root);
ArrayList<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>();
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
ans.add(node.val);
if (node.left != null) {
queue.add(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.add(node.right);
}
}
int[] res = new int[ans.size()];
for (int i = 0; i < ans.size(); i++) {
res[i] = ans.get(i);
}
return res;
}
题024二叉搜索树得后序遍历
输入一个整数数组,判断该数组是不是某二叉搜索树的后序遍历结果。如果是则返回 true,否则返回 false。假设输入的数组的任意两个数字都互不相同。
参考以下这颗二叉搜索树:
5
/ \
2 6
/ \
1 3
示例 1:
输入: [1,6,3,2,5]
输出: false
示例 2:
输入: [1,3,2,6,5]
输出: true
定义:
后续遍历:左 右 根
二叉搜索树:所有节点 左 < 根 < 右
递归分治
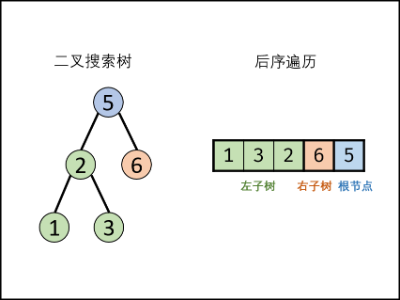
终止条件: 当 i ≥j ,说明此子树节点数量 ≤1 ,无需判别正确性,因此直接返回 true; 递推工作:
- 划分左右子树: 遍历后序遍历的 [i, j][i,j] 区间元素,寻找 第一个大于根节点 的节点,索引记为 m 。此时,可划分出左子树区间 [i,m-1][i,m−1] 、右子树区间 [m, j - 1][m,j−1] 、根节点索引 j 。
- 判断是否为二叉搜索树: 左子树区间 [i, m - 1][i,m−1] 内的所有节点都应 <postorder[j] 。而第 1.划分左右子树 步骤已经保证左子树区间的正确性,因此只需要判断右子树区间即可。 右子树区间 [m, j-1][m,j−1] 内的所有节点都应 >postorder[j] 。实现方式为遍历,当遇到≤postorder[j] 的节点则跳出;则可通过 p = j 判断是否为二叉搜索树。
返回值: 所有子树都需正确才可判定正确,因此使用 与逻辑符 \&& 连接。
- p = j : 判断 此树 是否正确。
- recur(i, m - 1): 判断 此树的左子树 是否正确。
- recur(m, j - 1): 判断 此树的右子树 是否正确。
public boolean verifyPostorder(int[] postorder) {
return recur(postorder, 0, postorder.length - 1);
}
boolean recur(int[] postorder, int i, int j) {
if (i >= j) { //节点数量<=1
return true;
}
int p = i;
while (postorder[p] < postorder[j]) {
p++;
}
int m = p; // 第一个大于根节点 可划分出左子树区间 [i,m-1][i,m−1] 、右子树区间 [m, j - 1][m,j−1] 、根节点索引 j 。
while (postorder[p] > postorder[j]) {
p++; //如过满足二叉搜索树定义 则继续++ 到根节点
}
// 判断该树 左 右 树是否正确
return p == j && recur(postorder, i, m - 1) && recur(postorder, m, j - 1);
}
题025二叉树中和为某一值的路径
输入一棵二叉树和一个整数,打印出二叉树中节点值的和为输入整数的所有路径。从树的根节点开始往下一直到叶节点所经过的节点形成一条路径。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ / \
7 2 5 1 返回:
[
[5,4,11,2],
[5,8,4,5]
]
解法:DFS+ 回溯
class Solution {
LinkedList<List<Integer>> res = new LinkedList<>();
LinkedList<Integer> path = new LinkedList<>();
public List<List<Integer>> pathSum(TreeNode root, int sum) {
recure(root, sum);
return res;
}
void recure(TreeNode root, int sum) {
if (root ==null ){ //结束条件
return;
}
path.add(root.val);
sum = sum - root.val;
if (sum == 0 && root.left == null && root.right == null) {
res.add(path);
}
recure(root.left, sum);
recure(root.right, sum);
path.removeLast(); //回溯把path元素移除
}
}